Why do most Social Media tools get Social Media Analytics wrong? Simple they report Numbers, not Narratives. Your social media analytics tool said ” you ‘re doing great” – but your audience just ghosted.Most social media tools miss the story behind statistics. Let’s fix that today.
In just 100 years, the way we communicate has gone through numerous evolutions. Radio, newspapers, and television were once the go-to mediums of one way-communication – with a limited scope of reach and passive user interaction. These traditional channels provided limited immediacy, minimal feedback loops, and restricted audience targeting.
But now, we are in an internet-based social media era that offers multi-way communication with real-time interactivity and content permanence. Today, social media is not just a platform to connect; it is a powerful ecosystem where real customers express their real opinions – instantly and publicly.
Businesses wield the power of social media to heed the opinions of customers by mining social networks. They gather information from customer opinions and make business decisions. Collecting the opinion of the customers, analyzing the data, and improving brand strategy is always a challenging task for brands. It is where social media analytic tools play a crucial role. The core of social media analytics are based on two primary social media mining techniques.
What are the Social Media Mining Techniques?
Social media mining is all about understanding the customers’ opinions and associated problems in the market. Graph mining and text mining are the two social media mining techniques used by companies to understand their customers better. Most social networks mine useful information with graph mining and text mining techniques.
Graph mining is the process of extracting useful knowledge from a social relationship using a social media graph search. This method helps to identify influencers, their interaction dynamics, and community structures.
Text mining is the process of extracting the meaning of the text from both structured and unstructured data present in social media. It is used for sentiment analysis, topic modeling, and understanding customer intent.
What are Social Media Analytics tool?
Social media analytics is the art and science of extracting valuable hidden insights from vast amounts of structured and semi-structured social media data. It enables informed and insightful decision-making. It involves the systemic identification, extraction, and analysis of social media data using sophisticated tools and techniques such as Natural Language Processing (NLP), machine learning, and real-time visualization platforms.
Why is Social Media Analytics Tools Important for Social Networks?
Social media has become mainstream, and people are using it to express their feelings, interests, and preferences. As a result, social media analytics is gaining prominence among both research and business sectors.
Businesses need to tap into the vast amounts of data produced by social media users to
- increase brand loyalty,
- generate leads,
- drive traffic,
- predict trends,
- ultimately for making strategic decisions rooted in consumer sentiment.
Social media data and users are of great value to businesses.
Purpose of Social Media Analytics
The main premise of social media analytics is to facilitate an informed and insightful decision-making process using social media data. The following are critical business questions for social media analytics.
- What are customers saying about our brand or a new product launch on social media?
- Which social media content resonates most with our audience?
- How can I harness social media data to improve products/ services?
- Is the social media conversation about our company, product, or service positive, negative, or neutral?
- How can I leverage social media to promote brand awareness?
- Who are our influential social media followers, fans, and friends?
- Which social media platforms are driving the most traffic to our corporate website?
- Where is the geographical location of our social media customers?
- Which keywords and terms are trending on social media?
- How are people connected to the brand?
- Which websites are connected to your corporate website?
- How are competitors performing on social media?
Nature of Social Media Data
Social media data typically includes
- Semi-structured formats ( e.g., hashtags and mentions)
- Real-time, user-generated content ( UGC)
- High-volume and highly diverse streams (e.g., live streams)
- Informal socialized expressions.
- Unpredictable diversified data based on tone, language, and context.
- Content that gains more value through sharing and amplifying ( e.g., trending videos).
Layers of Social Media Analytics
Analysts say that there are seven layers of data available in social media.
Each layer is found to have valuable insights and information that are harvested for business intelligence purposes. Out of the seven layers, some layers are visible, and some are invisible. The seven layers are
- Text – User comments, captions, and tweets come under the text.
- Hyperlinks – External links and click-through behavior are the hyperlinks.
- Actions – Audience reaction for the posts like shares, likes, retweets, and reactions comes under the action layer.
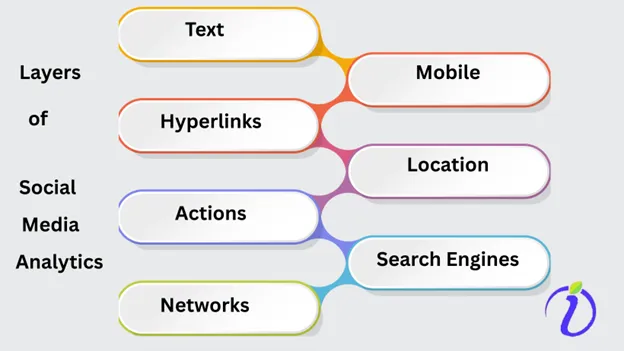
- Networks – New follower list, current friends list, and interaction graphs fall under the network layer.
- Mobile – Device-specific insights and app usage.
- Location – Geo-tagging and local trends.
- Search engines – Social SEO patterns and discoverability by search engines are the 7th layer.
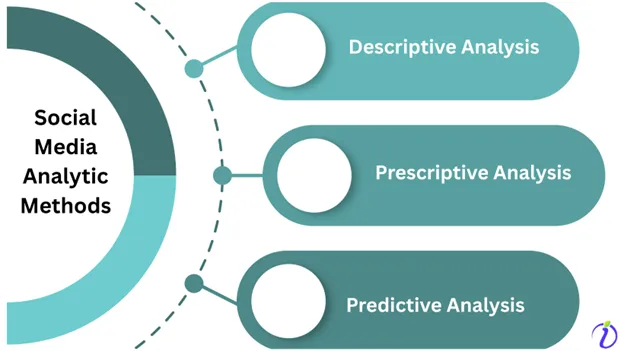
Social Media Management Tool Analytic Methods:
Social media tools separate the given data and typically analyze these seven layers. The following three analytic methods are used in the process.
- Descriptive Analysis:
Descriptive analysis focuses on gathering and describing the social media data in various report forms. Action analytics, such as the number of likes, views, and comments for a post and text analytics, are the best examples of descriptive analytics. Descriptive analytics is widely used in most social media management tools.
- Predictive Analysis:
When a large volume of data is to be analyzed, predictive analysis is used. To do so, predictive analysis uses a machine learning process to identify the patterns and predict future behavior.
- Prescriptive Analytics:
During a social scenario, prescriptive analytics move a step forward and suggest the best actions.
For example, A store research identifies a certain online buying pattern among their social media customers. In that case, prescriptive analysis will share the actions that can be taken in the future to capitalize on this pattern.
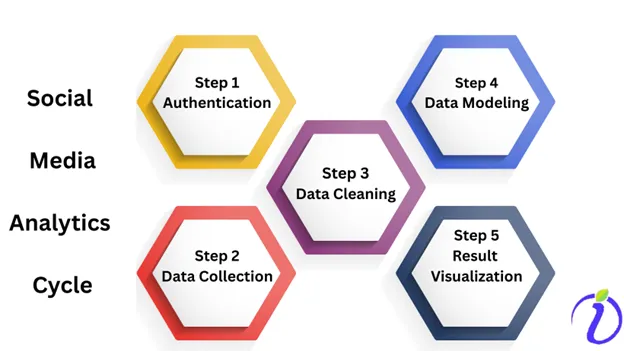
Social Media Analytics Cycle:
The five-step iterative process of mining social media data based on business insights is called social media analytics. There are general steps in social media analytics.
Step 1:
Authentication on Social Media:
Create an app on social media like Twitter or Facebook. Get API access keys and tokens.
Step 2:
Collect Data using API:
Collect both structured and unstructured data using API from social media.
Step 3:
Data Cleaning:
After the data is preprocessed and normalized, it is fed into the modeling algorithm.
Step 4:
Data modeling:
Data modeling uses opinion mining and recommendations for identifying patterns. This is the fourth step.
Step 5:
Result Visualization:
The last step in analytics is visualization. The results are viewed as graphs and charts in dashboards. Using the final output, the trends are analyzed.
Application of Social Media Analytics
- Twitter: Sentiment analysis
- Facebook Post Gender Analysis: Gender analysis of Facebook post likes.
- Facebook Friends Network Analysis.
What are the Challenges in Social Media Analytics?
Social media data analytics is a high volume, high velocity, and highly diverse data analysis and interpretation method. Analyzing unstructured data requires new tools and metrics with high capability for real-time analytics that most businesses do not possess.
- High Volume and High-Velocity Unstructured Data
Social media data is generated every second in large volumes. Capturing and analyzing these records is a real challenge.
Example: on Twitter, for every minute, 30,000 tweets appear, whereas on Facebook, one million likes are shared every twenty minutes.
- Content Diversity is a Challenge
Social media users generate extremely diverse, multilingual content in different formats and contexts. When one piece of content goes viral, there are more chances that it will be reproduced and shared in other contexts. To understand this complex model across different geographical locations, gender, language, and time, real-time analysis is required.

- Tool Limitations
Most social media analytics tools rely heavily on descriptive metrics. Marketeres receive only the surface-level reports of the brand. These reports lack deeper predictive and perspective insights and thus require real-time analysis.
- API Restrictions and Data Access
Rate-limit API calls and restricted data access make it hard for social media analytics tools to collect comprehensive datasets.
Why Do Most Social Media Management Tools Get Social Media Analytics Wrong?

Social Media Tools fall short in defining the strategies due to outdated technology, generic reporting, and wrong focus data.
1. Tracking the Wrong Metrics: When Numbers Don’t tell the full story
Most social media management tools still prioritize the wrong vanity metrics. Likes, impressions, and followers are easy to measure and look good on reports. But these numbers often mislead marketers.
| Vanity Metrics | Actionable Metrics |
|---|---|
| Follower Count | Audience Growth Rate |
| Post Likes | Engagement Rate per Follower |
| Reach | Click-Through Rate (CTR) |
| Impressions | Conversion Rate from Campaigns |
Example: Y Brand’s Instagram post gets 10K likes (vanity), but there were only 15 website clicks (actionable). The real insight lies in user behavior and not popularity.
2. Misreading Sentiment: When Tools Can’t Understand People
Basic sentiment analysis relies on keywords only. It lacks the nuance to interpret tone, emotion, sarcasm, slang, or ironic concepts.
| Tweet | Tool Sentiment Output | Actual Sentiment |
|---|---|---|
| Wow, that was a great crash | Positive | Negative |
| Sick Launch | Negative | Positive |
| I love how this app never works | Positive | Negative |
Tools need advanced NLP ( Natural Language Processing ) models to understand regional and platform-specific language patterns ( e.g., memes, emojis, and Gen Z slang).
3. Running Behind: Static Dashboards Vs Real-time Analytics
| Feature | Static Dashboard Tool | Real-time Analytics Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Data refresh rate | Hourly or daily | Every 5 to 15 minutes |
| Competitor analysis | Manual reports | Automated benchmarking |
| Trend detection | Delayed | Instant alerts |
| Crisis management capability | Low | High |
| Hashtag monitoring | Limited | Dynamic tracking |
Most social media analytics tools are built on batch processing. In this process, the data is collected, cleaned, and analyzed every few hours or once daily. It is not suitable for the fast-moving digital landscape. Real-time modeling is the only option for brands to act on trends before they peak rather than reacting after the damage is done.
4. Ignoring Industry Context – How is Success Defined?
Many social media tools offer pre-designed dashboards. The metrics and analysis patterns are the same, irrespective of the industry and niche. Hence, these reports pose a question of reliability for the brand. A B2B company wants lead generation and demo bookings, whereas a fashion brand looks for engagement and trend velocity.
| Industry | Required Metric |
|---|---|
| E-commerce | Cart Abandonment via Social Campaigns |
| SaaS | Sign-ups and Trial Conversions |
| Healthcare | Trust Sentiment & Compliance Mentions |
| Fashion | Trend Velocity & Influencer Performance |
Most generic tools do not capture these unique compliance, seasonality, and customer behavior differences. If there are no industry-specific KPIs, insights are just generic and disconnected from actual business goals.
5. Missing the competition: No Benchmarking Features
If there are no reference points to compare with the competitors in an evaluation, then the review is not valid. You need benchmarking features to understand whether the brand is thriving or simply maintaining the status quo.
Benchmarking helps you to identify the gaps, refine strategy, and stay ahead of the competition.
| Feature | Tool Without Benchmarking Features | Tool With Benchmarking Features |
|---|---|---|
| Context for performance | None | Relative to industry |
| Strategic adjustments | Based on assumptions | Based on proven gaps or strengths |
| Competitive trend tracking | Manual | Automated, real-time |
| Goal setting | Vague | Data-backed, market-specific |
Example:
A Fashion brand receives a 3% Instagram engagement rate on the first day and celebrates it as a milestone. The average engagement Instagram engagement rate is 6% for fashion brands during the same seasonal campaign. Without this context, the brand wastes time optimizing the wrong content.
Choose tools that have dynamic benchmarking features.
6. Fragmented Data: No Unified Customer View
Audiences will see your ad on social media, click the link, and visit your website. Once the product is satisfactory, they tend to purchase it. This is the online sales process. Most social media analytics tools stop tracking after a social media interaction, and there is no evidence of what happened next.
This creates Data Silos – Brand’s social metrics in one place, sales data in another section, and CRM records in the third section. If there is no integration between these three metrics, then brands fail to measure the actual ROI.
Brands need a unified system that bridges the gap between engagement and outcome.
| Aspect | Fragmented System | Integrated (Unified) System |
|---|---|---|
| Social metrics only | Likes, shares, comments | Combined with leads and conversions |
| Cross-channel visibility | Low | 360-degree view |
| Attribution accuracy | Poor | Accurate source-to-sale tracking |
| Data-driven decisions | Based on guesswork | Based on full-funnel analytics |
7. Poor Visualization: Charts, Charts and Charts
A beautiful chart is useless if it does not tell a clear story. Social media tools often rely on these charts for analysis. Oversimplification of the data or overwhelming users with cluttered visuals is of no use.
| Visualization Type | Decorative Charts | Actionable Dashboards |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Eye-catching | Insight-driven |
| Custom filters | Limited or none | Platform, region, time |
| Audience understanding | Generalized | Tailored per department |
| Follow-up actions | Not indicated | Clear next steps, alerts, or insights |
Visuals must motivate marketers to prompt action.
8. Platform API Limitations: The Data You Need Isn’t Always There
Social media tools are constrained by platform-level restrictions – such as limited access to metrics and private mentions.
| Criteria | Restricted API Access | Full (or Workaround-Enabled) Access |
|---|---|---|
| Instagram Stories | Limited (e.g., views only) | Add link tracking, UTM codes |
| Private group monitoring | Not available | Community tools or manual export |
| X engagement | Depends on rate limits | Requires tool updates or paid access |
Example:
A fashion brand runs a series of Instagram stories with product links. Generic social media analysis tools cannot track story replies or link taps due to API limitations. It concludes that the content underperformed. But in reality, the conversations had happened off the radar.
If the data pipeline is incomplete, even the best tool cannot give you full data coverage.
Choose a platform that has transparent platform coverage, link tracking, UTM integrations, and the ability to pull first-party data into the analysis.
What to Look for in the Right Social Media Analytics Tool
| Must-Have Features | Why It’s Important |
|---|---|
| Custom KPIs by Industry | Relevance to business goals |
| Contextual Sentiment Analysis | Accurate emotion and tone detection |
| Real-time Dashboards + Alerts | Timely action and trendspotting |
| Cross-platform Benchmarking | Strategic positioning vs competitors |
| CRM & Business Data Integration | Connect data to actual revenue |
| Flexible Visualizations | Actionable reporting for all teams |
To harness social media analytics, always
- Invest in tools with AI/ML-based contextual engines
- Prefer tools with customized dashboards
- Check for benchmarking and real-time alerts in the tool.
- Check for business data integration like sales, CRM, and product usage for true ROI insights.
Indzusocial platform is developed combining NLP, data science, and business intelligence layers. Check it out for a comprehensive, accurate view of your social presence.